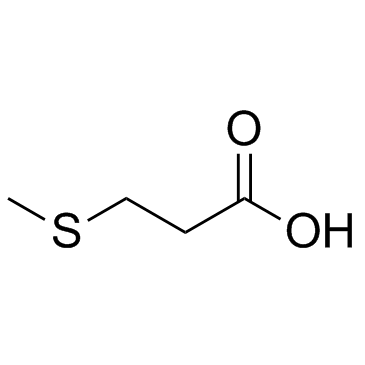
3-(Methylthio)propionic acid
CAS No. 646-01-5
3-(Methylthio)propionic acid( 3-Methylsulfanylpropionic acid | 3-Methylthiopropionate | 4-Thiapentanoic acid )
Catalog No. M20021 CAS No. 646-01-5
3-methylthiopropionate is one of the metabolites of methionine (especially of D-methionine). Cultures of Streptomyces lincolnensis accumulated 3-methylthioacrylic acid in amounts directly related to the concentration of methionine in the medium. The first intermediate in the pathway may be the keto acid which is then oxidatively decarboxylated to 3-methylthiopropionic acid.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 43 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name3-(Methylthio)propionic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description3-methylthiopropionate is one of the metabolites of methionine (especially of D-methionine). Cultures of Streptomyces lincolnensis accumulated 3-methylthioacrylic acid in amounts directly related to the concentration of methionine in the medium. The first intermediate in the pathway may be the keto acid which is then oxidatively decarboxylated to 3-methylthiopropionic acid.
-
Description3-methylthiopropionate is one of the metabolites of methionine (especially of D-methionine). Cultures of Streptomyces lincolnensis accumulated 3-methylthioacrylic acid in amounts directly related to the concentration of methionine in the medium. The first intermediate in the pathway may be the keto acid which is then oxidatively decarboxylated to 3-methylthiopropionic acid.
-
In VitroMethionine has consistently been shown to be the most toxic amino acid in experiments devised to assess the relative toxicity of dietary amino acids. 3-methylthiopropionate is an intermediate in methionine catabolism in rat and monkey liver in vitro. This pathway appears to account for a major portion of methionine oxidation in vitro. Cultures of Streptomyces lincolnensis accumulated 3-methylthioacrylic acid in amounts directly related to the concentration of methionine in the medium. The first intermediate in the pathway may be the keto acid, which is then oxidatively decarboxylated to 3-methylthiopropionic acid. The purified 3-MTPA has antifungal activity in assays using F. oxysporum as a model fungus. Daily measurements of shoot and root length shows severe inhibition of seed germination and root and shoot development at concentrations above 12mg for partially purified extracts. 3-methylthiopropionic acid ethyl ester possesses potential anticarcinogenic properties by inducing differentiation in well-differentiated colon cancer cells. Treatment of RCM-1 cells for 4 days with 3-methylthiopropionic acid ethyl ester between the doses of 0.25 and 2 mM progressively increases the percent area occupied by duct structures relative to the control, and also induces an increase in the number and the maximum diameter of the ducts in each culture plate.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms3-Methylsulfanylpropionic acid | 3-Methylthiopropionate | 4-Thiapentanoic acid
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number646-01-5
-
Formula Weight120.17
-
Molecular FormulaC4H8O2S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityH2O:25 mg/mL (208.04 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
SMILESCSCCC(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Surette R et al. Formation of 3-methylthioacrylic acid from methionine by Streptomyces lincolnensis. Isolation of a peroxidase. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1976 Jun;29(6):646-52.
molnova catalog



related products
-
3-Amino-2-oxazolidin...
3-Amino-2-oxazolidinone (AOZ) is the metabolite of Furazolidone. It is always be detected as a indicator of furazolidone residues in vivo.
-
UPF 1069
UPF 1069 is a specific PARP2 inhibitor ( IC50: 0.3 μM). It is ~27-fold selective against PARP1.
-
Echinocystic acid 28...
Echinocystic acid 28-O-β-D-glucoside is a metabolite resulting from the microbial oxidation and glucosidation of Echinocystic acid.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


